Viscose fabric is a semi-synthetic material made from cellulose, which comes from plants like bamboo, eucalyptus, or wood pulp.
This versatile fabric offers the softness and drape of silk at a more affordable price, making it popular in clothing and home decor.
Many people appreciate viscose for its lightweight feel and breathability, but it’s important to be aware of its care requirements and some drawbacks.
Table of contents
- Understanding Viscose Fabric
- The Manufacturing Process
- Environmental and Health Implications
- Care and Maintenance
- Applications of Viscose Fabric
- Benefits and Advantages
- Challenges and Limitations
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the primary uses of viscose fabric?
- How is viscose material produced?
- What are the environmental impacts of viscose production?
- How does viscose compare to polyester in terms of characteristics?
- What are the pros and cons of using viscose fabric?
- How does the breathability of viscose compare to other fabrics?
As you explore the world of viscose, you’ll find that it’s often compared to rayon, another fabric with similar properties. While both are derived from natural sources, viscose is known for its smooth texture and vibrant color retention, making it an appealing choice for various uses.
You might also discover its role in sustainable fashion, as more brands seek to balance style and environmental impact.
Whether you’re considering viscose for a new outfit or looking for ways to care for your favorite viscose pieces, this blog will guide you through essential facts and tips to help you make informed choices.
Understanding Viscose Fabric
Viscose fabric is a versatile textile known for its soft texture and draping qualities. It is made from regenerated cellulose fibers, which can come from various sources.
This section will explore its composition, how it compares to other fabrics, and the types of viscose available.
Composition and Characteristics
Viscose is primarily made from cellulose, a natural polymer found in plant cell walls. The production process involves dissolving cellulose in a viscous solution, often using chemicals like carbon disulfide and sodium hydroxide.
The result is a lightweight, breathable fabric that has a smooth, silk-like feel. Viscose is known for its vibrant colors and good draping qualities. It is also absorbent, making it suitable for warmer climates. However, it lacks the insulating properties of some other fabrics, like wool or cotton.
Comparison to Other Fabrics
When compared to cotton, viscose is generally less expensive to produce. It shares some qualities, such as softness and breathability, but does not insulate as well.
Unlike polyester and other synthetic fabrics, viscose is derived from natural fibers, giving it a more organic feel.
Viscose can mimic the look and feel of silk at a lower price point, making it a popular choice for dresses and blouses. It can also be blended with other fibers, such as modal or lyocell, to enhance its properties.
Keep in mind that viscose production can be less eco-friendly than cotton due to the chemicals used during manufacturing.
Types of Viscose
There are several types of viscose, each with distinct characteristics. Common types include:
- Viscose Rayon: This is the standard viscose, often used in clothing for its affordability and softness.
- Modal: A type of viscose made from beech trees, it is more durable and has better moisture-wicking properties.
- Lyocell (Tencel): This fabric is produced using a more eco-friendly process and offers higher strength and breathability.
- Cupro: A cellulose-derived fabric similar to silk that is often used for luxury clothing.
These types of viscose have different applications, making them suitable for various fashion items and home textiles.
The Manufacturing Process
| Feature | Viscose | Cotton | Silk | Polyester | Linen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Softness | Very soft, smooth | Soft, breathable | Extremely soft, luxurious | Can feel rough or synthetic | Crisp, gets softer over time |
| Breathability | Highly breathable | Highly breathable | Moderate | Low – can trap heat | Excellent |
| Moisture Absorption | Absorbs moisture well | Very absorbent | Highly absorbent | Poor – moisture-wicking | Very absorbent |
| Durability | Moderate | High | Delicate | Very high | High |
| Wrinkle Resistance | Prone to wrinkles | Some wrinkles | Wrinkles easily | Wrinkle-resistant | Wrinkles easily |
| Drape & Flow | Excellent drape, flowy | Moderate drape | Elegant, flowing drape | Stiff, lacks natural drape | Moderate drape |
| Eco-Friendliness | Semi-sustainable (wood pulp-based) | More sustainable (natural) | Sustainable but animal-based | Least eco-friendly (synthetic) | Highly sustainable (natural) |
| Best Used For | Dresses, blouses, scarves, activewear | Everyday wear, bedding, shirts | Luxury wear, formal dresses | Sportswear, budget clothing | Summer wear, home textiles |
Viscose fabric originates from natural materials and undergoes several steps to transform them into a usable textile. This section outlines the key stages involved in making viscose fabric, from raw materials to the final fibers.
Raw Materials and Chemicals
The main raw materials for viscose are wood pulp, often sourced from eucalyptus, bamboo, or sugar cane. These materials contain cellulose, which is the primary component needed for producing viscose.
In the initial stage, the wood is chipped into small pieces. It then undergoes treatment with chemicals.
Sodium hydroxide, also known as caustic soda, helps dissolve the cellulose in wood pulp. This creates a brown wood pulp solution. Carbon disulfide may also be used to transform the cellulose into a viscous liquid.
Extraction and Conversion of Cellulose
After preparing the wood pulp, the next step is to extract the cellulose. The brown wood pulp is washed and cleaned thoroughly, removing any impurities. This process is crucial for ensuring the quality of the final product.
Once cleaned, the cellulose is dissolved with sodium hydroxide. This forms a liquid solution rich in cellulose. The solution is then aged for a specific period to enhance its properties. Once ready, it is regenerated into a liquid state suitable for fiber production.
Spinning and Weaving
The viscous cellulose solution is then extruded through tiny holes in a spinneret. As the liquid passes through, it solidifies into thin strands, forming cellulose fibers. This part of the process is key for determining the thickness and quality of the final fabric.
After the fibers are created, they are washed and treated to remove any residual chemicals. Once cleaned, the fibers can be spun into yarn.
The yarn is then woven or knitted to create the final fabric. This final step combines durability with softness, making viscose suitable for a range of textile products.
Environmental and Health Implications

Viscose fabric’s production reveals significant environmental and health concerns. It involves toxic chemicals and raises questions about sustainability and ecosystem health. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed choices about this fabric.
Toxicity and Chemical Concerns
The production of viscose fabric often uses toxic chemicals, particularly carbon disulfide and caustic soda. Carbon disulfide can pose serious health risks to workers, including nerve damage and reproductive issues.
Proper regulation and certification can help mitigate these risks. However, many factories operate without strict oversight, leading to hazardous working conditions. The wastewater generated can also contain toxic runoff, impacting local water supplies and ecosystems.
Efforts to improve the safety of viscose production are ongoing, but challenges remain in ensuring all manufacturers adhere to environmental standards.
Ecosystem Impact and Sustainability
Viscose production has a notable impact on ecosystems, primarily due to deforestation. As raw materials like bamboo and eucalyptus trees are harvested, habitats are destroyed, and biodiversity suffers.
Though viscose is biodegradable and made from renewable resources, the cultivation practices can lead to unsustainable land use. Efforts to promote eco-friendly farming and certification systems are essential for improving sustainability.
Additionally, the energy used in processing viscose is less than that of polyester, but it still contributes to carbon emissions. Balancing production with environmental impact is crucial to achieving true sustainability in the fabric industry.
Care and Maintenance
| Care Aspect | Best Practices for Viscose Fabric |
|---|---|
| Washing | Hand wash in cold water with mild detergent |
| Machine Wash | Use a delicate cycle in cold water inside a mesh laundry bag |
| Drying | Lay flat to dry; avoid wringing or twisting |
| Ironing | Use low heat while slightly damp; place a cloth over the fabric to avoid damage |
| Wrinkle Removal | Steam lightly instead of ironing directly |
| Shrinkage | Viscose can shrink if exposed to hot water; always use cold water wash |
| Bleaching | Avoid bleach—it weakens the fibers |
| Dry Cleaning | Preferred for delicate viscose garments |
| Storage | Store in a cool, dry place; avoid hanging heavy garments to prevent stretching |
| Stain Removal | Blot stains gently with cold water and mild detergent; avoid scrubbing |
Viscose fabric requires careful handling to maintain its softness and durability. Proper washing and storage techniques can prevent shrinkage and wrinkling, helping your garments last longer.
Washing and Cleaning
When washing viscose, it’s best to hand wash in cold water using a mild detergent. This method helps protect the fabric’s strength and color retention.
If you prefer using a washing machine, select a gentle cycle and place your viscose items in a mesh laundry bag to prevent damage.
After washing, avoid wringing the fabric, as this can cause it to lose its shape. Instead, gently squeeze out excess water and lay the item flat on a clean towel.
To remove wrinkles, consider using a clothes steamer or setting your iron to a medium heat with a pressing cloth.
Storage and Lifespan
To keep your viscose fabrics in good condition, store them in a cool, dry place.
Avoid hanging viscose garments for long periods, as this can stretch the fabric. Instead, fold them neatly and place them in a drawer or on a shelf.
Viscose is not as durable as some other fabrics, so be mindful of how often you wear and wash these items. Proper care can extend the lifespan of your viscose clothing. For occasional deep cleaning, consider dry cleaning to help maintain the fabric’s quality.
Applications of Viscose Fabric
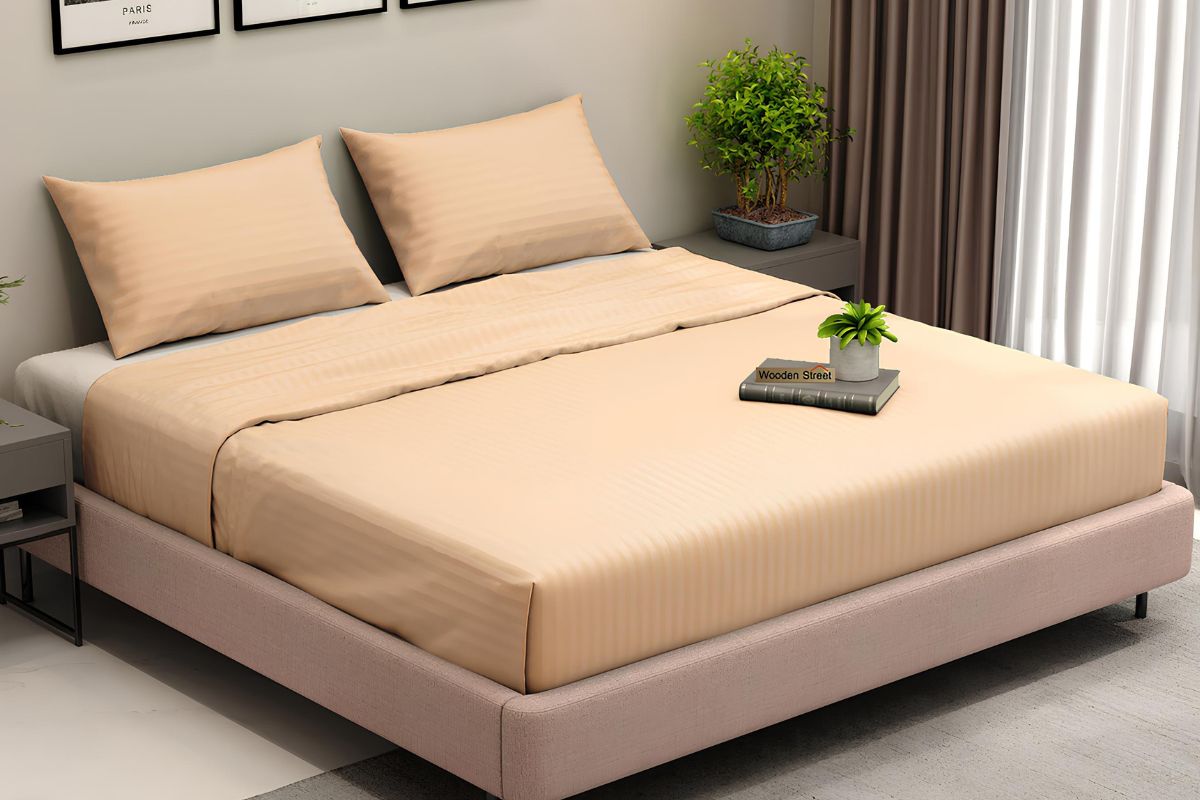

Viscose fabric is known for its softness and versatility, making it ideal for various applications in both fashion and home textiles. Its unique properties allow it to be used in a wide range of products that appeal to different needs and preferences.
Fashion and Apparel
In the fashion industry, viscose fabric is widely used for clothing items. Its soft texture and ability to drape well make it perfect for:
- Dresses: Viscose is often used in flowing dresses that require a comfortable feel and an elegant look.
- Blouses: Many blouses feature viscose for its lightweight quality and smooth finish.
- Lingerie and Activewear: It provides a pleasant sensation against the skin, ideal for close-fitting garments.
Viscose can also mimic the appearance of silk, adding to its appeal in clothing. With various patterns and colors, you can find viscose in trendy designs that suit any occasion.
Home Textiles and Decor
Viscose is not just limited to clothing; it is also popular in home textiles. Its properties allow it to be used in several products, including:
- Curtains: Viscose drapes beautifully, making it a great choice for window treatments that enhance natural light.
- Cushion Covers: The fabric’s soft feel adds comfort to cushions while also allowing for vibrant patterns and colors.
- Bed Linens: You might find viscose blends in bed linens, providing a luxurious sleeping experience.
This versatility makes viscose a favored option for various home decor items, blending style with functionality.
Benefits and Advantages
| Feature | Benefits & Advantages of Viscose Fabric |
|---|---|
| Softness | Feels smooth and luxurious, similar to silk |
| Breathability | Highly breathable, keeping you cool & comfortable |
| Moisture Absorption | Absorbs sweat well, making it great for warm weather |
| Drape & Flow | Elegant drape, making it ideal for stylish clothing |
| Lightweight | Feels airy and soft on the skin |
| Versatility | Used for clothing, home textiles, and accessories |
| Eco-Friendliness | Made from natural wood pulp, more sustainable than synthetics |
| Color Retention | Holds dyes well, resulting in vibrant and long-lasting colors |
| Affordable | Provides a luxurious feel at a lower cost than silk |
| Blending Ability | Blends well with cotton, polyester, and spandex for improved performance |
Viscose fabric offers several benefits that make it a popular choice in the fashion industry. Its softness and breathability provide superior comfort, while its affordability makes it a practical option for many consumers. These qualities contribute to its appeal for various clothing items.
Comfort and Wearability
Viscose is known for its softness and breathable qualities, making it a comfortable option for clothing. It feels smooth against your skin, much like silk, which enhances your wearing experience.
This fabric is also moisture-absorbent, allowing it to wick sweat away, keeping you dry in warm conditions. Its airy nature contributes to a feeling of relaxation, which can be particularly beneficial during hot weather or while engaging in physical activities.
Moreover, viscose drapes beautifully, allowing garments to flow elegantly. This draping quality adds to the overall comfort, giving you a stylish yet cozy feel in your clothing choices.
Economic and Aesthetic Value
Viscose is an affordable alternative to more expensive materials like silk. Many fashion items use viscose to provide similar luxurious appearances without the high price tag.
Its versatility is another advantage; viscose can easily be blended with other fibers. This blend can enhance other properties, such as durability and stretch, making garments more functional.
The fabric’s ability to hold dyes well means that you can enjoy vibrant colors and patterns. This makes viscose a favored choice in the fashion industry, where style and affordability are important for consumers.
Challenges and Limitations

Viscose fabric faces significant challenges, particularly concerning its environmental impact and material properties.
Understanding these limitations is essential for making informed choices about using this textile.
Environmental Concerns
The production of viscose involves severe environmental issues. It starts with sourcing wood pulp from trees like pine and spruce.
This extraction can lead to deforestation and habitat loss.
Moreover, the chemical process used to create viscose involves toxic chemicals. These chemicals can contaminate local water sources, creating a situation where wastewater poses risks to aquatic life and ecosystems.
Even with advancements like modal and lyocell, which use more sustainable methods, traditional viscose still lacks the eco-friendly reputation many consumers seek today.
Sustainable practices are necessary to reduce these environmental impacts and ensure a healthier planet.
Material Properties
Viscose fabric has notable material properties that come with challenges.
While it is known for its soft texture and excellent drape, its durability is often questioned.
Viscose tends to be less strong than cotton or polyester, which can affect its lifespan.
Notably, it loses strength when wet. This characteristic can lead to wear and tear more rapidly than with synthetic materials.
Another concern is its high flammability. Proper care and treatment are essential to decrease the risks associated with its use.
While viscose is absorbent and good at regulating moisture and body heat, its weaknesses mean you may need to handle it with greater care than other fabrics.
Frequently Asked Questions
Viscose fabric is a versatile material with many uses and a unique production process. Understanding its impacts and characteristics can help you make informed choices about its use in clothing and other products.
What are the primary uses of viscose fabric?
Viscose is commonly used in clothing such as blouses, dresses, and linings. It is valued for its soft feel and drape, making it suitable for casual and formal wear. Viscose is also used in home textiles like curtains and bed linens.
How is viscose material produced?
Viscose is produced from wood pulp through a chemical process. The cellulose fibers are treated with chemicals to create a viscous solution. This solution is then spun into threads, which are woven or knitted to form the fabric.
What are the environmental impacts of viscose production?
The production of viscose can have negative environmental effects. It often involves high concentrations of chemicals that can pollute water sources.
Additionally, deforestation for wood pulp sourcing raises concerns about habitat destruction and biodiversity loss.
How does viscose compare to polyester in terms of characteristics?
Viscose is softer and more breathable than polyester, making it more comfortable in warm weather.
Polyester, however, is more durable and resistant to wrinkles. Each fabric has its advantages based on the intended use.
What are the pros and cons of using viscose fabric?
Pros of viscose include its affordability, softness, and ability to drape well. On the downside, it can wrinkle easily and requires careful washing. Viscose also tends to absorb moisture, which may not be ideal in all situations.
How does the breathability of viscose compare to other fabrics?
Viscose is generally breathable, similar to cotton. It allows air to circulate, making it a good choice for warm climates.
Compared to materials like polyester, viscose provides better comfort and reduces the risk of overheating.